We often emphasize the geospatial analysis capability of our products and solutions. In this article, we explain the details of the geospatial analysis feature and its contributions to your analysis.
Geospatial analysis is an analysis method that allows obtaining location-based insights and reaches conclusions by running data on maps. It is a system that is based on the collection, display, and processing of location-based data or geographic data such as street addresses, zip codes, satellite images, and GPS coordinates. This analysis method supports obtaining location-based results by combining geospatial data with other business data on the map.
Although there are products developed exclusively for spatial analysis, this feature provides a stronger analysis experience when integrated into data analytics systems such as business intelligence. With the increase in the number of smart devices, the amount and variety of geographic data also increase. Thus, when business data supported by location-based data combine with a powerful analysis system, provides users to reach the most accurate results.
A combination of comprehensive geospatial analysis infrastructure and data analytics system provides not only comprehensive map support, but also rich geo-based visualization. The ability to analyse data on a map and support for geographic calculations such as intersection, junction, and distance calculations enable to reveal solutions and insights that are geographically related to each other and location-oriented. Carrying out existing analyses on the map also enables stronger reporting and tracking. In order to achieve the analysis goal, regional data can be detailed, advantageous regions can be discovered, and regional problems can be revealed by geospatial analysis. Solutions for location-based problems also provide significant financial advantages to institutions. For example, geospatial data are frequently used in logistics planning to save fuel and time.
While choosing the right geospatial analysis solution, the features we have detailed below are crucial in terms of carrying out the analysis in the most accurate way. The spatial analysis capabilities of our products have all these capabilities and more.
It is the ability to autofill and update dashboards and maps with data about specific places and areas for use in spatial analysis. It allows searching by city, county, zip code, place names, or airport codes.
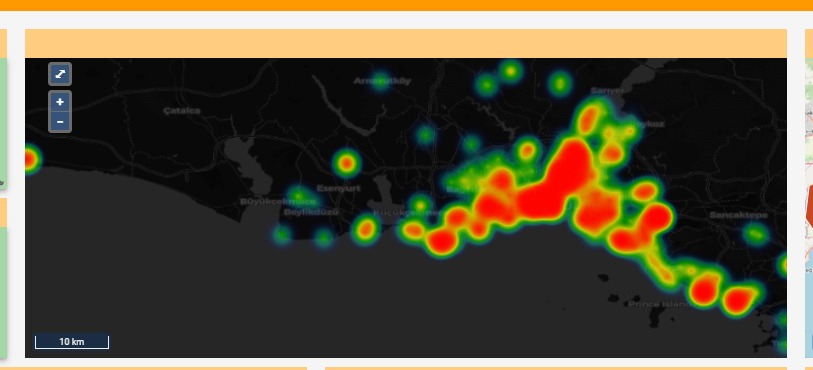
By visualizing groups of high or low values that stand out in the data, their geographic density can be displayed with the clustering capability.

Colours, lines, and shapes make data more understandable. For example, our BI solutions have rich formatting tools such as different colors options to distinguish between demographic data and explore their geographic distribution. The data can be presented in different colours and formats by their status as province/district, demographic characteristics.
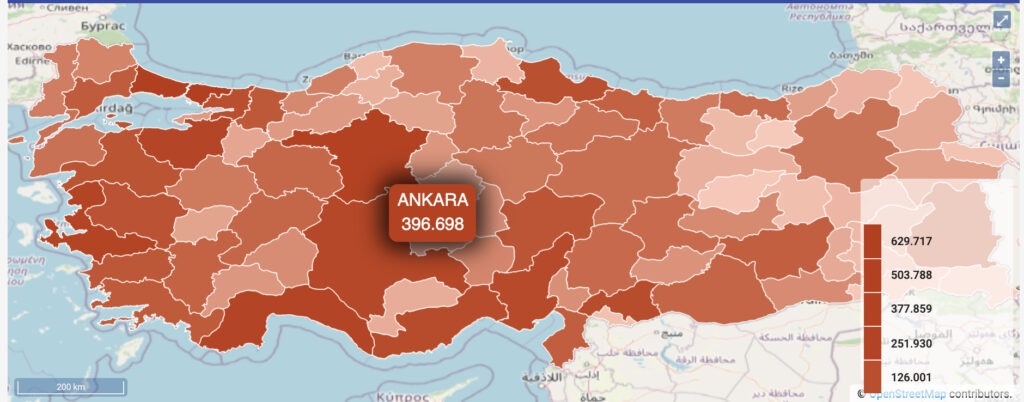
This feature allows all data to be updated instantly in keeping with the selected location. For example, by selecting a specific region or province/district, all information in the dashboard can be updated instantly.
By selecting the region to be focused on with Datactive’s selection tool, the data of the relevant region can be accessed. This feature is particularly effective for intelligence analysis. In the pursuit of suspicious people or vehicles, monitoring the paths of these people and their activities as meeting with other suspects supports analysts in solving lots of crimes.
This support provides that constantly updated data is reflected in the analysis instantly. This simultaneity is important, especially in cases that are tracked geographically. In our systems, instant data is already reflected in the analytics. Likewise, in the geographical analysis option, users can work on updated data.
Geographic analysis tools help display and analyse multiple datasets in different layers on maps. Layers are placed on background maps and may include area, balloon, graph, geodata, heatmap, and line layers. Data for background maps and layers can be obtained from both internal and external sources.
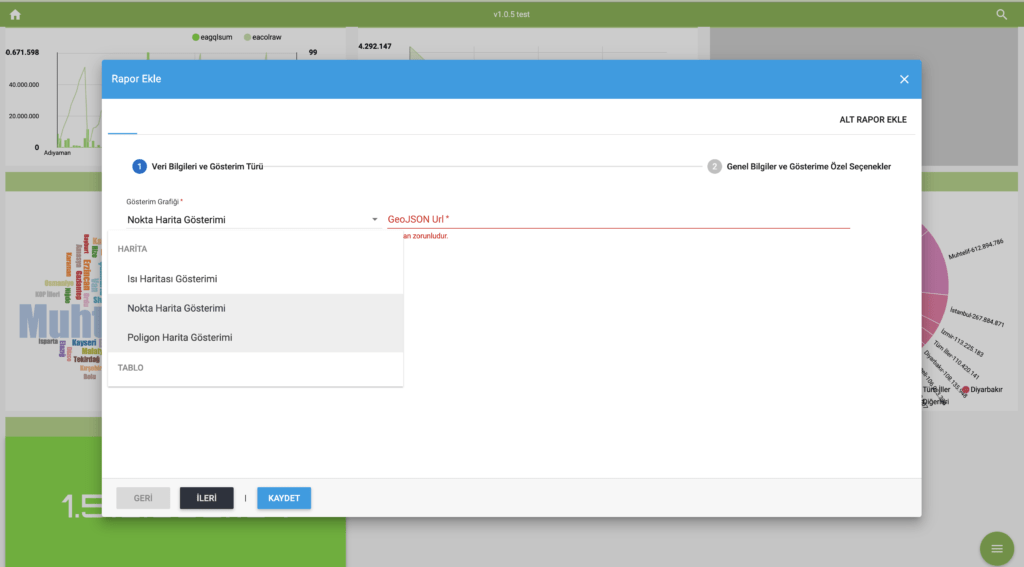
Geodata are generally obtained from a variety of sources, both internal and external. They are often stored in specific formats on different systems, and it makes them difficult to access and use. Embedded geospatial analysis capability helps standardize and filter data from different sources to make it ready for analysis. Map analyses can be extended by dynamically adding WMS and WFS data sources. In offline systems, the user’s own map bases can be used.
All these features and more are available in the spatial analysis feature of our solutions. Both of our products offer the most comprehensive data analytics service without the need for a third-party plug-in. You can contact us for detailed information.